ICGOO在线商城 > 集成电路(IC) > PMIC - 稳压器 - DC DC 开关稳压器 > TC7660EOA713
- 型号: TC7660EOA713
- 制造商: Microchip
- 库位|库存: xxxx|xxxx
- 要求:
| 数量阶梯 | 香港交货 | 国内含税 |
| +xxxx | $xxxx | ¥xxxx |
查看当月历史价格
查看今年历史价格
TC7660EOA713产品简介:
ICGOO电子元器件商城为您提供TC7660EOA713由Microchip设计生产,在icgoo商城现货销售,并且可以通过原厂、代理商等渠道进行代购。 TC7660EOA713价格参考。MicrochipTC7660EOA713封装/规格:PMIC - 稳压器 - DC DC 开关稳压器, 固定 充电泵 开关稳压器 IC 正或负 -Vin,2Vin 1 输出 20mA 8-SOIC(0.154",3.90mm 宽)。您可以下载TC7660EOA713参考资料、Datasheet数据手册功能说明书,资料中有TC7660EOA713 详细功能的应用电路图电压和使用方法及教程。
TC7660EOA713 是由 Microchip Technology 生产的一款 PMIC(电源管理集成电路),属于 DC-DC 开关稳压器类别。该器件具有高效能和灵活性,适用于多种应用场景。 应用场景 1. 便携式电子设备: - TC7660EOA713 适用于需要高效电源管理的便携式设备,如智能手机、平板电脑、智能手表等。它能够提供稳定的电压输出,确保设备在不同负载条件下正常工作。 - 该器件的小尺寸和低功耗特性使其非常适合对空间和电池寿命有严格要求的便携式应用。 2. 工业自动化: - 在工业环境中,TC7660EOA713 可用于为传感器、执行器和其他控制设备供电。其高效率和宽输入电压范围使其能够在复杂的工业环境中稳定工作。 - 该器件还可以用于工业通信模块,如 RS-485 或 CAN 总线接口,提供所需的电源转换。 3. 消费电子产品: - 在消费电子产品中,TC7660EOA713 可以为各种外围设备提供稳定的电源,如 USB 接口、音频放大器、显示屏背光等。 - 它还适用于智能家居设备,如智能灯泡、智能插座等,提供高效且可靠的电源管理。 4. 汽车电子: - 在汽车电子系统中,TC7660EOA713 可用于为车载信息娱乐系统、导航系统、车身控制模块等提供电源。 - 其宽温度范围和抗电磁干扰能力使其能够在严苛的汽车环境中稳定工作。 5. 医疗设备: - 在医疗设备中,TC7660EOA713 可以为便携式医疗仪器、监护设备、可穿戴健康监测设备等提供稳定的电源。 - 该器件的高可靠性和低噪声特性对于医疗设备的精确测量至关重要。 总结 TC7660EOA713 凭借其高效、灵活和可靠的特点,广泛应用于便携式电子设备、工业自动化、消费电子产品、汽车电子和医疗设备等领域。它不仅能够提供稳定的电源输出,还能满足不同应用场景下的特殊需求,是现代电子系统中不可或缺的关键组件。
| 参数 | 数值 |
| 产品目录 | 集成电路 (IC)半导体 |
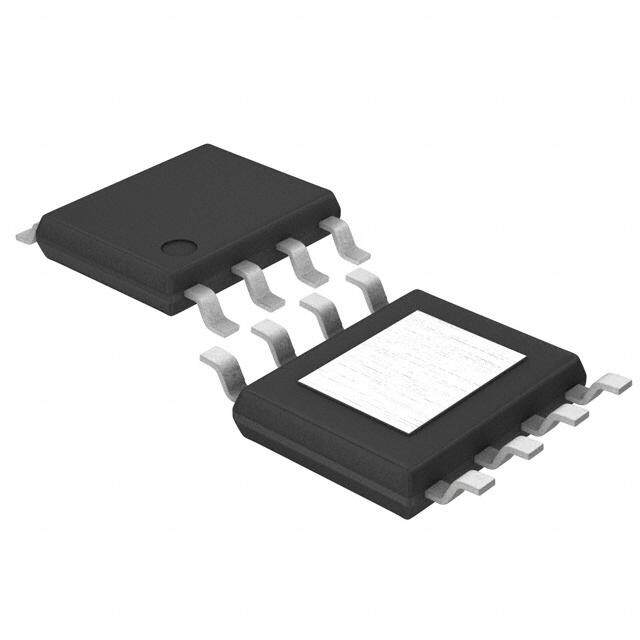
| 描述 | IC REG SWITCHD CAP INV ADJ 8SOIC稳压器—开关式稳压器 DC-DC Converter |
| 产品分类 | |
| 品牌 | Microchip Technology |
| 产品手册 | |
| 产品图片 |
|
| rohs | 符合RoHS无铅 / 符合限制有害物质指令(RoHS)规范要求 |
| 产品系列 | 电源管理 IC,稳压器—开关式稳压器,Microchip Technology TC7660EOA713- |
| 数据手册 | http://www.microchip.com/mymicrochip/filehandler.aspx?ddocname=en011631 |
| 产品型号 | TC7660EOA713 |
| PCN组件/产地 | http://www.microchip.com/mymicrochip/NotificationDetails.aspx?id=5774&print=view |
| PCN设计/规格 | http://www.microchip.com/mymicrochip/NotificationDetails.aspx?id=5704&print=view |
| PWM类型 | - |
| 产品种类 | 稳压器—开关式稳压器 |
| 供应商器件封装 | 8-SOIC N |
| 关闭 | No Shutdown |
| 包装 | 带卷 (TR) |
| 同步整流器 | 无 |
| 商标 | Microchip Technology |
| 安装类型 | 表面贴装 |
| 安装风格 | SMD/SMT |
| 宽度 | 3.91 mm |
| 封装 | Reel |
| 封装/外壳 | 8-SOIC(0.154",3.90mm 宽) |
| 封装/箱体 | SOIC-8 Narrow |
| 工作温度 | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 工厂包装数量 | 3300 |
| 开关频率 | 10 kHz |
| 拓扑结构 | Inverting |
| 最大工作温度 | + 85 C |
| 最大输入电压 | 10 V |
| 最小工作温度 | - 40 C |
| 标准包装 | 3,300 |
| 电压-输入 | 1.5 V ~ 10 V |
| 电压-输出 | -1.5 V ~ -10 V |
| 电流-输出 | 20mA |
| 电源电流 | 80 uA |
| 类型 | Boost Regulator |
| 输入电压 | 1.5 V to 10 V |
| 输出数 | 1 |
| 输出电压 | - 1.5 V to - 10 V |
| 输出电流 | 20 mA |
| 输出类型 | 可调式 |
| 频率-开关 | 10kHz |






- 商务部:美国ITC正式对集成电路等产品启动337调查
- 曝三星4nm工艺存在良率问题 高通将骁龙8 Gen1或转产台积电
- 太阳诱电将投资9.5亿元在常州建新厂生产MLCC 预计2023年完工
- 英特尔发布欧洲新工厂建设计划 深化IDM 2.0 战略
- 台积电先进制程称霸业界 有大客户加持明年业绩稳了
- 达到5530亿美元!SIA预计今年全球半导体销售额将创下新高
- 英特尔拟将自动驾驶子公司Mobileye上市 估值或超500亿美元
- 三星加码芯片和SET,合并消费电子和移动部门,撤换高东真等 CEO
- 三星电子宣布重大人事变动 还合并消费电子和移动部门
- 海关总署:前11个月进口集成电路产品价值2.52万亿元 增长14.8%



PDF Datasheet 数据手册内容提取
TC7660 Charge Pump DC-to-DC Voltage Converter Features Package Types • Wide Input Voltage Range: +1.5V to +10V PDIP/CERDIP/SOIC • Efficient Voltage Conversion (99.9%, typ) • Excellent Power Efficiency (98%, typ) NC 1 8 V+ • Low Power Consumption: 80µA (typ) @ V = 5V IN CAP+ 2 7 OSC • Low Cost and Easy to Use TC7660 LOW - Only Two External Capacitors Required GND 3 6 VOLTAGE (LV) • Available in 8-Pin Small Outline (SOIC), 8-Pin CAP- 4 5 VOUT PDIP and 8-Pin CERDIP Packages • Improved ESD Protection (3kV HBM) • No External Diode Required for High-Voltage General Description Operation The TC7660 device is a pin-compatible replacement Applications for the industry standard 7660 charge pump voltage converter. It converts a +1.5V to +10V input to a corre- • RS-232 Negative Power Supply sponding -1.5V to -10V output using only two low-cost • Simple Conversion of +5V to ±5V Supplies capacitors, eliminating inductors and their associated • Voltage Multiplication VOUT = ± n V+ cost, size and electromagnetic interference (EMI). • Negative Supplies for Data Acquisition Systems The on-board oscillator operates at a nominal fre- and Instrumentation quency of 10kHz. Operation below 10kHz (for lower supply current applications) is possible by connecting an external capacitor from OSC to ground. The TC7660 is available in 8-Pin PDIP, 8-Pin Small Outline (SOIC) and 8-Pin CERDIP packages in commercial and extended temperature ranges. Functional Block Diagram V+CAP+ 8 2 OSC 7 OsRciCllator 2 VLoeltavegle 4 CAP- Translator 6 LV 5 V OUT IInntteerrnnaall VVooltltaaggee RReegguulalatotror Logic Network TC7660 3 GND 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 1
TC7660 1.0 ELECTRICAL * Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum Rat- ings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a CHARACTERISTICS stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those indicated in the Absolute Maximum Ratings* operational sections of this specification is not intended. Expo- Supply Voltage.............................................................+10.5V sure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. LV and OSC Inputs Voltage: (Note1) ..............................................-0.3V to V for V+ < 5.5V SS .....................................(V+ – 5.5V) to (V+) for V+ > 5.5V I Current into LV.........................................20µA for V+ > 3.5V 1 8 S Output Short Duration (VSUPPLY 5.5V)...............Continuous 2 7 I V+ Package Power Dissipation: (TA 70°C) C1 + 3 TC7660 6 COSCL (+5V) 8-Pin CERDIP....................................................800mW 10µF 8-Pin PDIP.........................................................730mW 4 5 RL 8-Pin SOIC.........................................................470mW Operating Temperature Range: VOUT C Suffix.......................................................0°C to +70°C I Suffix.....................................................-25°C to +85°C C2 E Suffix....................................................-40°C to +85°C + 10µF M Suffix.................................................-55°C to +125°C Storage Temperature Range.........................-65°C to +160°C FIGURE 1-1: TC7660 Test Circuit. ESD protection on all pins (HBM)................................. 3kV Maximum Junction Temperature.................................. 150°C ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, specifications measured over operating temperature range with V+ = 5V, C = 0, refer to test circuit in Figure1-1. OSC Parameters Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions Supply Current I+ — 80 180 µA R = L + Supply Voltage Range, High V H 3.0 — 10 V Min TAMax, RL = 10k, LV Open + Supply Voltage Range, Low V L 1.5 — 3.5 V Min TAMax, RL = 10k, LV to GND Output Source Resistance R — 70 100 I =20mA, T = +25°C OUT OUT A — — 120 I =20mA, T +70°C (C Device) OUT A — — 130 I =20mA, T +85°C (E and I Device) OUT A — 104 150 I =20mA, T +125°C (M Device) OUT A — 150 300 V+ = 2V, I = 3mA, LV to GND OUT 0°C T +70°C A — 160 600 V+ = 2V, I = 3mA, LV to GND OUT -55°C T +125°C (M Device) A Oscillator Frequency f — 10 — kHz Pin 7 open OSC Power Efficiency P 95 98 — % R = 5k EFF L Voltage Conversion Efficiency V 97 99.9 — % R = OUTEFF L Oscillator Impedance Z — 1.0 — M V+ = 2V OSC — 100 — k V+ = 5V Note 1: Destructive latch-up may occur if voltages greater than V+ or less than GND are supplied to any input pin. DS21465C-page 2 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 2.0 TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES Note: The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range. Note: Unless otherwise indicated, C = C = 10 µF, ESR = ESR = 1, T = 25°C. See Figure1-1. 1 2 C1 C2 A 12 100 %) 10 CY ( 98 IOUT = 1 mA N 96 GE (V) 8 FFICIE 94 A E 92 OLT 6 ON 90 IOUT = 15 mA V SI PLY 4 SUPPLY VOLTAGE RANGE VER 88 UP ON 86 S C 2 R 84 E OW 82 V+ = +5V 0 P 80 -55 -25 0 +25 +50 +75 +100 +125 100 1k 10k TEMPERATURE (°C) OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY (Hz) FIGURE 2-1: Operating Voltage vs. FIGURE 2-4: Power Conversion Temperature. Efficiency vs. Oscillator Frequency. 10k 500 Ω) Ω) IOUT = 1 mA E ( E (450 C C N N A A400 ST 1k ST SI SI E E200 R R E E RC RC150 OU100Ω OU V+ = +2V T S T S100 PU PU V + = +5V T T 50 U U O O 10Ω 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 -55 -25 0 +25 +50 +75 +100+125 SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V) TEMPERATURE (°C) FIGURE 2-2: Output Source Resistance FIGURE 2-5: Output Source Resistance vs. Supply Voltage. vs. Temperature. 10k V+ = +5V 20 V+ = +5V Y (Hz) Y (kHz) 18 NC 1k NC 16 E E U U Q Q 14 RE RE OR F OR F 12 OSCILLAT100 OSCILLAT 108 10 6 1 10 100 1000 10k -55 -25 0 +25 +50 +75 +100 +125 OSCILLATOR CAPACITANCE (pF) TEMPERATURE (°C) FIGURE 2-3: Frequency of Oscillation vs. FIGURE 2-6: Unloaded Oscillator Oscillator Capacitance. Frequency vs. Temperature. 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 3
TC7660 Note: Unless otherwise indicated, C = C = 10 µF, ESR = ESR = 1, T = 25°C. See Figure1-1. 1 2 C1 C2 A 0 5 V+ = +5V -1 4 -2 3 E (V) -3 E (V) 2 AG -4 AG 1 T T OL -5 OL 0 V V T -6 T -1 U U TP -7 TP -2 U U O -8 O -3 -9 -4 SLOPE 55Ω LV OPEN -10 -5 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90100 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 OUTPUT CURRENT (mA) LOAD CURRENT (mA) FIGURE 2-7: Output Voltage vs. Output FIGURE 2-10: Output Voltage vs. Load Current. Current. 100 20 100 100 Y (%) 90 V+ = 2V 18 Y (%) 90 90 ENC 80 16 A) ENC 80 80 A) N EFFICI 6700 1124 RENT (m N EFFICI 6700 6700 RENT (m O 50 10 R O 50 50 R ERSI 40 8 Y CU ERSI 40 40 Y CU V L V L ON 30 6 PP ON 30 30 PP R C 20 4 SU R C 20 20 SU E E OW 10 2 OW 10 V+ = +5V 10 P 0 P 0 0 1.5 3.0 4.5 6.0 7.5 9.0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 LOAD CURRENT (mA) LOAD CURRENT (mA) FIGURE 2-8: Supply Current and Power FIGURE 2-11: Supply Current and Power Conversion Efficiency vs. Load Current. Conversion Efficiency vs. Load Current. 2 V+ = +2V V) 1 E ( G A T OL 0 V T U P T U -1 O SLOPE 150Ω -2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 LOAD CURRENT (mA) FIGURE 2-9: Output Voltage vs. Load Current. DS21465C-page 4 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 3.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS The descriptions of the pins are listed in Table3-1. TABLE 3-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE Pin No. Symbol Description 1 NC No connection 2 CAP+ Charge pump capacitor positive terminal 3 GND Ground terminal 4 CAP- Charge pump capacitor negative terminal 5 V Output voltage OUT 6 LV Low voltage pin. Connect to GND for V+ < 3.5V 7 OSC Oscillator control input. Bypass with an external capacitor to slow the oscillator 8 V+ Power supply positive voltage input 3.1 Charge Pump Capacitor (CAP+) 3.5 Low Voltage Pin (LV) Positive connection for the charge pump capacitor, or The low voltage pin ensures proper operation of the flying capacitor, used to transfer charge from the input internal oscillator for input voltages below 3.5V. The low source to the output. In the voltage-inverting configura- voltage pin should be connected to ground (GND) for tion, the charge pump capacitor is charged to the input input voltages below 3.5V. Otherwise, the low voltage voltage during the first half of the switching cycle. Dur- pin should be allowed to float. ing the second half of the switching cycle, the charge pump capacitor is inverted and charge is transferred to 3.6 Oscillator Control Input (OSC) the output capacitor and load. The oscillator control input can be utilized to slow down It is recommended that a low ESR (equivalent series or speed up the operation of the TC7660. Refer to resistance) capacitor be used. Additionally, larger Section5.4 “Changing the TC7660 Oscillator Fre- values will lower the output resistance. quency”, for details on altering the oscillator frequency. 3.2 Ground (GND) 3.7 Power Supply (V+) Input and output zero volt reference. Positive power supply input voltage connection. It is 3.3 Charge Pump Capacitor (CAP-) recommended that a low ESR (equivalent series resis- tance) capacitor be used to bypass the power supply Negative connection for the charge pump capacitor, or input to ground (GND). flying capacitor, used to transfer charge from the input to the output. Proper orientation is imperative when using a polarized capacitor. 3.4 Output Voltage (V ) OUT Negative connection for the charge pump output capacitor. In the voltage-inverting configuration, the charge pump output capacitor supplies the output load during the first half of the switching cycle. During the second half of the switching cycle, charge is restored to the charge pump output capacitor. It is recommended that a low ESR (equivalent series resistance) capacitor be used. Additionally, larger values will lower the output ripple. 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 5
TC7660 4.0 DETAILED DESCRIPTION EQUATION 1 4.1 Theory of Operation ROUT = f-----------------------C----1--+8RSW+4ESRC1+ESRC2 PUMP The TC7660 charge pump converter inverts the voltage applied to the V+ pin. The conversion consists of a two- Where: phase operation (Figure4-1). During the first phase, f aswreit cchloesse dS.2 C an cdh Sar4g aerse t oo ptheen vaonltda gsew iatcphpelise dS t1o a tnhde VS3+ fPUMP = --O---2-S---C-- 1 R = on-resistance of the switches pin, with the load current being supplied from C . Dur- SW 2 ESR = equivalent series resistance of C ing the second phase, switches S and S are closed C1 1 2 4 and switches S1 and S3 are open. Charge is trans- ESRC2 = equivalent series resistance of C2 ferred from C to C , with the load current being 1 2 supplied from C . 1 4.2 Switched Capacitor Inverter Power Losses S S 1 2 V+ The overall power loss of a switched capacitor inverter + is affected by four factors: C 1 1. Losses from power consumed by the internal oscillator, switch drive, etc. These losses will + vary with input voltage, temperature and C GND S S 2 oscillator frequency. 3 4 VOUT = -VIN 2. Conduction losses in the non-ideal switches. 3. Losses due to the non-ideal nature of the external capacitors. 4. Losses that occur during charge transfer from C to C when a voltage difference between the 1 2 capacitors exists. FIGURE 4-1: Ideal Switched Capacitor Figure4-3 depicts the non-ideal elements associated Inverter. with the switched capacitor inverter power loss. In this manner, the TC7660 performs a voltage inver- sion, but does not provide regulation. The average out- S S put voltage will drop in a linear manner with respect to R 1 R 2 SW SW load current. The equivalent circuit of the charge pump inverter can be modeled as an ideal voltage source in series with a resistor, as shown in Figure4-2. V+ IDD C1 + C2 + + I LOAD - OUT R ESR ESR OUT C1 C2 V OUT S S - R 3 R 4 SW SW V+ + FIGURE 4-3: Non-Ideal Switched Capacitor Inverter. FIGURE 4-2: Switched Capacitor Inverter The power loss is calculated using the following Equivalent Circuit Model. equation: The value of the series resistor (R ) is a function of OUT the switching frequency, capacitance and equivalent EQUATION series resistance (ESR) of C and C and the on-resis- 1 2 tance of switches S1, S2, S3 and S4. A close P = I2 R +I V+ LOSS OUT OUT DD approximation for R is given in the following OUT equation: DS21465C-page 6 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 5.0 APPLICATIONS INFORMATION 5.2 Paralleling Devices To reduce the value of R , multiple TC7660 voltage 5.1 Simple Negative Voltage OUT converters can be connected in parallel (Figure5-2). Converter The output resistance will be reduced by approximately Figure5-1 shows typical connections to provide a a factor of n, where n is the number of devices negative supply where a positive supply is available. A connected in parallel. similar scheme may be employed for supply voltages EQUATION anywhere in the operating range of +1.5V to +10V, keeping in mind that pin 6 (LV) is tied to the supply R = ------R----O---U----T------o----f- --T----C----7----6---6---0--------- negative (GND) only for supply voltages below 3.5V. OUT nnumber of devices V+ While each device requires its own pump capacitor (C ), all devices may share one reservoir capacitor 1 1 8 (C ). To preserve ripple performance, the value of C 2 2 2 7 V * should be scaled according to the number of devices + OUT C1 3 TC7660 6 C2 connected in parallel. 10µF + 10µF 4 5 5.3 Cascading Devices * V = -V+ for 1.5V V+ 10V A larger negative multiplication of the initial supply volt- OUT age can be obtained by cascading multiple TC7660 FIGURE 5-1: Simple Negative Converter. devices. The output voltage and the output resistance will both increase by approximately a factor of n, where The output characteristics of the circuit in Figure5-1 n is the number of devices cascaded. are those of a nearly ideal voltage source in series with a 70resistor. Thus, for a load current of -10mA and EQUATION a supply voltage of +5V, the output voltage would be + -4.3V. V = –nV OUT R = nR of TC7660 OUT OUT V+ 1 8 2 7 1 8 + TC7660 C1 3 6 2 7 RL + TC7660 4 “1” 5 C1 3 6 4 “n” 5 C 2 + FIGURE 5-2: Paralleling Devices Lowers Output Impedance. V+ 1 8 2 7 1 8 + TC7660 10µF 3 6 2 7 + TC7660 4 “1” 5 10µF 3 6 4 “n” 5 VOUT * 10µF + 10µF + * V = -n V+ for 1.5V V+ 10V OUT FIGURE 5-3: Increased Output Voltage By Cascading Devices. 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 7
TC7660 5.4 Changing the TC7660 Oscillator 5.5 Positive Voltage Multiplication Frequency Positive voltage multiplication can be obtained by The operating frequency of the TC7660 can be employing two external diodes (Figure5-6). Refer to changed in order to optimize the system performance. the theory of operation of the TC7660 (Section4.1 The frequency can be increased by over-driving the “Theory of Operation”). During the half cycle when OSC input (Figure5-4). Any CMOS logic gate can be switch S2 is closed, capacitor C1 of Figure5-6 is utilized in conjunction with a 1k series resistor. The charged up to a voltage of V+ - VF1, where VF1 is the resistor is required to prevent device latch-up. While forward voltage drop of diode D1. During the next half TTL level signals can be utilized, an additional 10k cycle, switch S1 is closed, shifting the reference of pull-up resistor to V+ is required. Transitions occur on capacitor C1 from GND to V+. The energy in capacitor the rising edge of the clock input. The resultant output C1 is transferred to capacitor C2 through diode D2, pro- voltage ripple frequency is one half the clock input. ducing an output voltage of approximately: Higher clock frequencies allow for the use of smaller pump and reservoir capacitors for a given output volt- EQUATION age ripple and droop. Additionally, this allows the TC7660 to be synchronized to an external clock, V = 2V+–V +V OUT F1 F2 eliminating undesirable beat frequencies. where: At light loads, lowering the oscillator frequency can V is the forward voltage drop of diode D F1 1 increase the efficiency of the TC7660 (Figure5-5). By and lowering the oscillator frequency, the switching losses V is the forward voltage drop of diode D . F2 2 are reduced. Refer to Figure2-3 to determine the typi- cal operating frequency based on the value of the external capacitor. At lower operating frequencies, it V+ may be necessary to increase the values of the pump and reservoir capacitors in order to maintain the 1 8 desired output voltage ripple and output impedance. 2 TC7660 7 D1 D V(2O VU+T) = - (2 V ) V+ V+ 3 6 2 F 4 5 + + 1 8 C C 1k 1 2 CMOS 2 7 + TC7660 GATE 10µF 3 6 FIGURE 5-6: Positive Voltage Multiplier. 4 “1” 5 VOUT 5.6 Combined Negative Voltage 10µF + Conversion and Positive Supply Multiplication FIGURE 5-4: External Clocking. Simultaneous voltage inversion and positive voltage multiplication can be obtained (Figure5-7). Capacitors C and C perform the voltage inversion, while capaci- 1 3 1 8 V+ tors C2 and C4, plus the two diodes, perform the posi- tive voltage multiplication. Capacitors C and C are 1 2 2 7 + TC7660 the pump capacitors, while capacitors C3 and C4 are C1 3 6 COSC the reservoir capacitors for their respective functions. Both functions utilize the same switches of the TC7660. 4 5 VOUT As a result, if either output is loaded, both outputs will C2 drop towards GND. + FIGURE 5-5: Lowering Oscillator Frequency. DS21465C-page 8 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 V+ V OUT 1 8 = -V+ 2 7 + C3 TC7660 D 3 6 1 + 4 5 VOUT = C1 + D2 (2 V+) - (2 VF) C + 2 C 4 FIGURE 5-7: Combined Negative Converter and Positive Multiplier. 5.7 Efficient Positive Voltage Multiplication/Conversion Since the switches that allow the charge pumping operation are bidirectional, the charge transfer can be performed backwards as easily as forwards. Figure5-8 shows a TC7660 transforming -5V to +5V (or +5V to +10V, etc.). The only problem here is that the internal clock and switch-drive section will not operate until some positive voltage has been generated. An ini- tial inefficient pump, as shown in Figure5-7, could be used to start this circuit up, after which it will bypass the other (D and D in Figure5-7 would never turn on), or 1 2 else the diode and resistor shown dotted in Figure5-8 can be used to “force” the internal regulator on. V = -V- OUT 1 8 + 2 7 10µF C1 + TC7660 1M 10µF 3 6 4 5 V- input FIGURE 5-8: Positive Voltage Conversion. 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 9
TC7660 6.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION 6.1 Package Marking Information 8-Lead PDIP (300 mil) Example Example XXXXXXXX TC7660 TC7660 XXXXXNNN CPA e 3 256 CPA256 YYWW 1208 1208 8-Lead CERDIP (.300”) Example Example XXXXXXXX TC7660 TC7660 XXXXXNNN MJA e 3 256 MJA256 YYWW 1208 1208 8-Lead SOIC (3.90 mm) Example Example TC7660C TC7660C OA e 3 1208 OA1208 NNN 256 256 Legend: XX...X Customer-specific information Y Year code (last digit of calendar year) YY Year code (last 2 digits of calendar year) WW Week code (week of January 1 is week ‘01’) NNN Alphanumeric traceability code e3 Pb-free JEDEC designator for Matte Tin (Sn) * This package is Pb-free. The Pb-free JEDEC designator ( e 3 ) can be found on the outer packaging for this package. Note: In the event the full Microchip part number cannot be marked on one line, it will be carried over to the next line thus limiting the number of available characters for customer specific information. DS21465C-page 10 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 (cid:2)(cid:3)(cid:4)(cid:5)(cid:6)(cid:7)(cid:8)(cid:9)(cid:10)(cid:6)(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:8)(cid:15)(cid:16)(cid:6)(cid:10)(cid:8)(cid:17)(cid:18)(cid:3)(cid:4)(cid:13)(cid:18)(cid:5)(cid:8)(cid:19)(cid:9)(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:8)(cid:22)(cid:8)(cid:23)(cid:24)(cid:24)(cid:8)(cid:25)(cid:13)(cid:10)(cid:8)(cid:26)(cid:27)(cid:7)(cid:28)(cid:8)(cid:29)(cid:9)(cid:15)(cid:17)(cid:9)(cid:30) (cid:31)(cid:27)(cid:12)(cid:5) 4(cid:22)(cid:21)(cid:14)&(cid:23)(cid:13)(cid:14)’(cid:22)!&(cid:14)(cid:20)"(cid:21)(cid:21)(cid:13)(cid:25)&(cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:13)(cid:14)#(cid:21)(cid:11)*(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)!((cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:26)(cid:13)(cid:11)!(cid:13)(cid:14)!(cid:13)(cid:13)(cid:14)&(cid:23)(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:18)(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:10)(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:10)(cid:13)(cid:20)(cid:19)%(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:11)&(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)(cid:14)(cid:26)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:11)&(cid:13)#(cid:14)(cid:11)&(cid:14) (cid:23)&&(cid:10)366***(cid:29)’(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:10)(cid:29)(cid:20)(cid:22)’6(cid:10)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12) N NOTE1 E1 1 2 3 D E A A2 L A1 c e eB b1 b 7(cid:25)(cid:19)&! (cid:28)8,9.(cid:3) (cid:2)(cid:19)’(cid:13)(cid:25)!(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)(cid:14):(cid:19)’(cid:19)&! (cid:18)(cid:28)8 8;(cid:18) (cid:18)(cid:7)< 8"’)(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14)(cid:22)%(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:19)(cid:25)! 8 = (cid:31)(cid:19)&(cid:20)(cid:23) (cid:13) (cid:29)(cid:30)(cid:4)(cid:4)(cid:14)2(cid:3), (cid:24)(cid:22)(cid:10)(cid:14)&(cid:22)(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:13)(cid:11)&(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:26)(cid:11)(cid:25)(cid:13) (cid:7) > > (cid:29)(cid:16)(cid:30)(cid:4) (cid:18)(cid:22)(cid:26)#(cid:13)#(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:24)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:20)5(cid:25)(cid:13)!! (cid:7)(cid:16) (cid:29)(cid:30)(cid:30)1 (cid:29)(cid:30)-(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:30)(cid:6)1 2(cid:11)!(cid:13)(cid:14)&(cid:22)(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:13)(cid:11)&(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:26)(cid:11)(cid:25)(cid:13) (cid:7)(cid:30) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:30)1 > > (cid:3)(cid:23)(cid:22)"(cid:26)#(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14)&(cid:22)(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:23)(cid:22)"(cid:26)#(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14)?(cid:19)#&(cid:23) . (cid:29)(cid:16)(cid:6)(cid:4) (cid:29)-(cid:30)(cid:4) (cid:29)-(cid:16)1 (cid:18)(cid:22)(cid:26)#(cid:13)#(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:13)(cid:14)?(cid:19)#&(cid:23) .(cid:30) (cid:29)(cid:16)(cid:5)(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:16)1(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:16)=(cid:4) ; (cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:11)(cid:26)(cid:26)(cid:14):(cid:13)(cid:25)(cid:12)&(cid:23) (cid:2) (cid:29)-(cid:5)= (cid:29)-(cid:15)1 (cid:29)(cid:5)(cid:4)(cid:4) (cid:24)(cid:19)(cid:10)(cid:14)&(cid:22)(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:13)(cid:11)&(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:26)(cid:11)(cid:25)(cid:13) : (cid:29)(cid:30)(cid:30)1 (cid:29)(cid:30)-(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:30)1(cid:4) :(cid:13)(cid:11)#(cid:14)(cid:24)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:20)5(cid:25)(cid:13)!! (cid:20) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:4)= (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:30)(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:30)1 7(cid:10)(cid:10)(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14):(cid:13)(cid:11)#(cid:14)?(cid:19)#&(cid:23) )(cid:30) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:5)(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:15)(cid:4) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:17)(cid:4) :(cid:22)*(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14):(cid:13)(cid:11)#(cid:14)?(cid:19)#&(cid:23) ) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:30)(cid:5) (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:30)= (cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:16)(cid:16) ; (cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:11)(cid:26)(cid:26)(cid:14)(cid:8)(cid:22)*(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:10)(cid:11)(cid:20)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:14)+ (cid:13)2 > > (cid:29)(cid:5)-(cid:4) (cid:31)(cid:27)(cid:12)(cid:5)(cid:11) (cid:30)(cid:29) (cid:31)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:14)(cid:30)(cid:14) (cid:19)!"(cid:11)(cid:26)(cid:14)(cid:19)(cid:25)#(cid:13)$(cid:14)%(cid:13)(cid:11)&"(cid:21)(cid:13)(cid:14)’(cid:11)(cid:27)(cid:14) (cid:11)(cid:21)(cid:27)((cid:14))"&(cid:14)’"!&(cid:14))(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:26)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:11)&(cid:13)#(cid:14)*(cid:19)&(cid:23)(cid:14)&(cid:23)(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:23)(cid:11)&(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:13)#(cid:14)(cid:11)(cid:21)(cid:13)(cid:11)(cid:29) (cid:16)(cid:29) +(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:19)(cid:12)(cid:25)(cid:19)%(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:11)(cid:25)&(cid:14),(cid:23)(cid:11)(cid:21)(cid:11)(cid:20)&(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:19)!&(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:29) -(cid:29) (cid:2)(cid:19)’(cid:13)(cid:25)!(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)!(cid:14)(cid:2)(cid:14)(cid:11)(cid:25)#(cid:14).(cid:30)(cid:14)#(cid:22)(cid:14)(cid:25)(cid:22)&(cid:14)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:20)(cid:26)"#(cid:13)(cid:14)’(cid:22)(cid:26)#(cid:14)%(cid:26)(cid:11)!(cid:23)(cid:14)(cid:22)(cid:21)(cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:21)(cid:22)&(cid:21)"!(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)!(cid:29)(cid:14)(cid:18)(cid:22)(cid:26)#(cid:14)%(cid:26)(cid:11)!(cid:23)(cid:14)(cid:22)(cid:21)(cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:21)(cid:22)&(cid:21)"!(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)!(cid:14)!(cid:23)(cid:11)(cid:26)(cid:26)(cid:14)(cid:25)(cid:22)&(cid:14)(cid:13)$(cid:20)(cid:13)(cid:13)#(cid:14)(cid:29)(cid:4)(cid:30)(cid:4)/(cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14)!(cid:19)#(cid:13)(cid:29) (cid:5)(cid:29) (cid:2)(cid:19)’(cid:13)(cid:25)!(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:11)(cid:25)#(cid:14)&(cid:22)(cid:26)(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:11)(cid:25)(cid:20)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:14)(cid:7)(cid:3)(cid:18).(cid:14)0(cid:30)(cid:5)(cid:29)1(cid:18)(cid:29) 2(cid:3),3(cid:14)2(cid:11)!(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:14)(cid:2)(cid:19)’(cid:13)(cid:25)!(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)(cid:29)(cid:14)(cid:24)(cid:23)(cid:13)(cid:22)(cid:21)(cid:13)&(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:11)(cid:26)(cid:26)(cid:27)(cid:14)(cid:13)$(cid:11)(cid:20)&(cid:14) (cid:11)(cid:26)"(cid:13)(cid:14)!(cid:23)(cid:22)*(cid:25)(cid:14)*(cid:19)&(cid:23)(cid:22)"&(cid:14)&(cid:22)(cid:26)(cid:13)(cid:21)(cid:11)(cid:25)(cid:20)(cid:13)!(cid:29) (cid:18)(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:10)(cid:24)(cid:13)(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:25)(cid:22)(cid:26)(cid:22)(cid:12)(cid:27)(cid:2)(cid:21)(cid:11)*(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12),(cid:4)(cid:5)(cid:9)(cid:4)(cid:30)=2 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 11
TC7660 Note: For the most current package drawings, please see the Microchip Packaging Specification located at http://www.microchip.com/packaging DS21465C-page 12 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 Note: For the most current package drawings, please see the Microchip Packaging Specification located at http://www.microchip.com/packaging 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 13
TC7660 Note: For the most current package drawings, please see the Microchip Packaging Specification located at http://www.microchip.com/packaging DS21465C-page 14 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 (cid:2)(cid:3)(cid:4)(cid:5)(cid:6)(cid:7)(cid:8)(cid:9)(cid:10)(cid:6)(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:8)!(cid:25)(cid:6)(cid:10)(cid:10)(cid:8)"(cid:16)(cid:12)(cid:10)(cid:13)(cid:18)(cid:5)(cid:8)(cid:19)"(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:8)(cid:22)(cid:8)(cid:31)(cid:6)##(cid:27)$%(cid:8)(cid:23)&’(cid:24)(cid:8)(cid:25)(cid:25)(cid:8)(cid:26)(cid:27)(cid:7)(cid:28)(cid:8)(cid:29)!"(cid:17)((cid:30) (cid:31)(cid:27)(cid:12)(cid:5) 4(cid:22)(cid:21)(cid:14)&(cid:23)(cid:13)(cid:14)’(cid:22)!&(cid:14)(cid:20)"(cid:21)(cid:21)(cid:13)(cid:25)&(cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:13)(cid:14)#(cid:21)(cid:11)*(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)!((cid:14)(cid:10)(cid:26)(cid:13)(cid:11)!(cid:13)(cid:14)!(cid:13)(cid:13)(cid:14)&(cid:23)(cid:13)(cid:14)(cid:18)(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:10)(cid:14)(cid:31)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12)(cid:14)(cid:3)(cid:10)(cid:13)(cid:20)(cid:19)%(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:11)&(cid:19)(cid:22)(cid:25)(cid:14)(cid:26)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:11)&(cid:13)#(cid:14)(cid:11)&(cid:14) (cid:23)&&(cid:10)366***(cid:29)’(cid:19)(cid:20)(cid:21)(cid:22)(cid:20)(cid:23)(cid:19)(cid:10)(cid:29)(cid:20)(cid:22)’6(cid:10)(cid:11)(cid:20)5(cid:11)(cid:12)(cid:19)(cid:25)(cid:12) 2002-2011 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 15
TC7660 APPENDIX A: REVISION HISTORY Revision C (March 2012) The following is the list of modifications. 1. Updated Figure5-5. 2. Added Appendix A. Revision B (March 2003) Undocumented changes. Revision A (May 2002) Original release of this document. DS21465C-page 16 2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
TC7660 PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office. PART NO. X /XX Examples: a) TC7660COA: Commercial Temp., SOIC Device Temperature Package package. Range b) TC7660COA713:Tape and Reel, Commercial Temp., SOIC package. c) TC7660CPA: Commercial Temp., PDIP Device: TC7660: DC-to-DC Voltage Converter package. d) TC7660EOA: Extended Temp., SOIC package. Temperature Range: C = 0°C to +70°C e) TC7660EOA713:Tape and Reel, Extended E = -40°C to +85°C Temp., SOIC package. I = -25°C to +85°C (CERDIP only) f) TC7660EPA: Extended Temp., PDIP M = -55°C to +125°C (CERDIP only) package. g) TC7660IJA: Industrial Temp., CERDIP package Package: PA = Plastic DIP, (300 mil body), 8-lead h) TC7660MJA: Military Temp., CERDIP JA = Ceramic DIP, (300 mil body), 8-lead package. OA = SOIC (Narrow), 8-lead OA713 = SOIC (Narrow), 8-lead (Tape and Reel) 2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 17
TC7660 NOTES: DS21465C-page 18 2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices: • Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet. • Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the intended manner and under normal conditions. • There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property. • Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code. • Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.” Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act. Information contained in this publication regarding device Trademarks applications and the like is provided only for your convenience The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, dsPIC, and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to KEELOQ, KEELOQ logo, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART, ensure that your application meets with your specifications. PIC32 logo, rfPIC and UNI/O are registered trademarks of MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR countries. IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION, FilterLab, Hampshire, HI-TECH C, Linear Active Thermistor, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION, MXDEV, MXLAB, SEEVAL and The Embedded Control QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR Solutions Company are registered trademarks of Microchip FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, chipKIT, devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at chipKIT logo, CodeGuard, dsPICDEM, dsPICDEM.net, the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend, indemnify and dsPICworks, dsSPEAK, ECAN, ECONOMONITOR, hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims, FanSense, HI-TIDE, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, suits, or expenses resulting from such use. No licenses are Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPLAB Certified logo, MPLIB, conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip MPLINK, mTouch, Omniscient Code Generation, PICC, intellectual property rights. PICC-18, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, PICkit, PICtail, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries. SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies. © 2002-2012, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the U.S.A., All Rights Reserved. Printed on recycled paper. ISBN: 978-1-62076-089-5 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2009 certification for its worldwide headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in Chandler and CERTIFIED BY DNV Tempe, Arizona; Gresham, Oregon and design centers in California and India. The Company’s quality system processes and procedures == ISO/TS 16949 == are for its PIC® MCUs and dsPIC® DSCs, KEELOQ® code hopping devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified. 2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21465C-page 19
Worldwide Sales and Service AMERICAS ASIA/PACIFIC ASIA/PACIFIC EUROPE Corporate Office Asia Pacific Office India - Bangalore Austria - Wels 2355 West Chandler Blvd. Suites 3707-14, 37th Floor Tel: 91-80-3090-4444 Tel: 43-7242-2244-39 Chandler, AZ 85224-6199 Tower 6, The Gateway Fax: 91-80-3090-4123 Fax: 43-7242-2244-393 Tel: 480-792-7200 Harbour City, Kowloon India - New Delhi Denmark - Copenhagen Fax: 480-792-7277 Hong Kong Tel: 91-11-4160-8631 Tel: 45-4450-2828 Technical Support: Tel: 852-2401-1200 Fax: 91-11-4160-8632 Fax: 45-4485-2829 http://www.microchip.com/ support Fax: 852-2401-3431 India - Pune France - Paris Web Address: Australia - Sydney Tel: 91-20-2566-1512 Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 www.microchip.com Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 91-20-2566-1513 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755 Germany - Munich Atlanta Japan - Osaka Duluth, GA China - Beijing Tel: 81-66-152-7160 Tel: 49-89-627-144-0 Tel: 86-10-8569-7000 Fax: 49-89-627-144-44 Tel: 678-957-9614 Fax: 81-66-152-9310 Fax: 678-957-1455 Fax: 86-10-8528-2104 Japan - Yokohama Italy - Milan China - Chengdu Tel: 39-0331-742611 Boston Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Tel: 86-28-8665-5511 Fax: 39-0331-466781 Westborough, MA Fax: 81-45-471-6122 Tel: 774-760-0087 Fax: 86-28-8665-7889 Korea - Daegu Netherlands - Drunen Fax: 774-760-0088 China - Chongqing Tel: 82-53-744-4301 Tel: 31-416-690399 Chicago Tel: 86-23-8980-9588 Fax: 82-53-744-4302 Fax: 31-416-690340 Itasca, IL Fax: 86-23-8980-9500 Korea - Seoul Spain - Madrid Tel: 630-285-0071 China - Hangzhou Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Tel: 34-91-708-08-90 Fax: 630-285-0075 Tel: 86-571-2819-3187 Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or Fax: 34-91-708-08-91 Cleveland Fax: 86-571-2819-3189 82-2-558-5934 UK - Wokingham Independence, OH China - Hong Kong SAR Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur Tel: 44-118-921-5869 Tel: 216-447-0464 Tel: 852-2401-1200 Tel: 60-3-6201-9857 Fax: 44-118-921-5820 Fax: 216-447-0643 Fax: 852-2401-3431 Fax: 60-3-6201-9859 Dallas China - Nanjing Malaysia - Penang Addison, TX Tel: 86-25-8473-2460 Tel: 60-4-227-8870 Tel: 972-818-7423 Fax: 86-25-8473-2470 Fax: 60-4-227-4068 Fax: 972-818-2924 China - Qingdao Philippines - Manila Detroit Tel: 86-532-8502-7355 Tel: 63-2-634-9065 Farmington Hills, MI Fax: 86-532-8502-7205 Fax: 63-2-634-9069 Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260 China - Shanghai Singapore Tel: 86-21-5407-5533 Tel: 65-6334-8870 Indianapolis Fax: 86-21-5407-5066 Fax: 65-6334-8850 Noblesville, IN Tel: 317-773-8323 China - Shenyang Taiwan - Hsin Chu Fax: 317-773-5453 Tel: 86-24-2334-2829 Tel: 886-3-5778-366 Fax: 86-24-2334-2393 Fax: 886-3-5770-955 Los Angeles Mission Viejo, CA China - Shenzhen Taiwan - Kaohsiung Tel: 949-462-9523 Tel: 86-755-8203-2660 Tel: 886-7-536-4818 Fax: 949-462-9608 Fax: 86-755-8203-1760 Fax: 886-7-330-9305 Santa Clara China - Wuhan Taiwan - Taipei Santa Clara, CA Tel: 86-27-5980-5300 Tel: 886-2-2500-6610 Tel: 408-961-6444 Fax: 86-27-5980-5118 Fax: 886-2-2508-0102 Fax: 408-961-6445 China - Xian Thailand - Bangkok Toronto Tel: 86-29-8833-7252 Tel: 66-2-694-1351 Mississauga, Ontario, Fax: 86-29-8833-7256 Fax: 66-2-694-1350 Canada China - Xiamen Tel: 905-673-0699 Tel: 86-592-2388138 Fax: 905-673-6509 Fax: 86-592-2388130 China - Zhuhai Tel: 86-756-3210040 11/29/11 Fax: 86-756-3210049 DS21465C-page 20 2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.

 Datasheet下载
Datasheet下载

