ICGOO在线商城 > 传感器,变送器 > 运动传感器 - 加速计 > LIS331HH
- 型号: LIS331HH
- 制造商: STMicroelectronics
- 库位|库存: xxxx|xxxx
- 要求:
| 数量阶梯 | 香港交货 | 国内含税 |
| +xxxx | $xxxx | ¥xxxx |
查看当月历史价格
查看今年历史价格
LIS331HH产品简介:
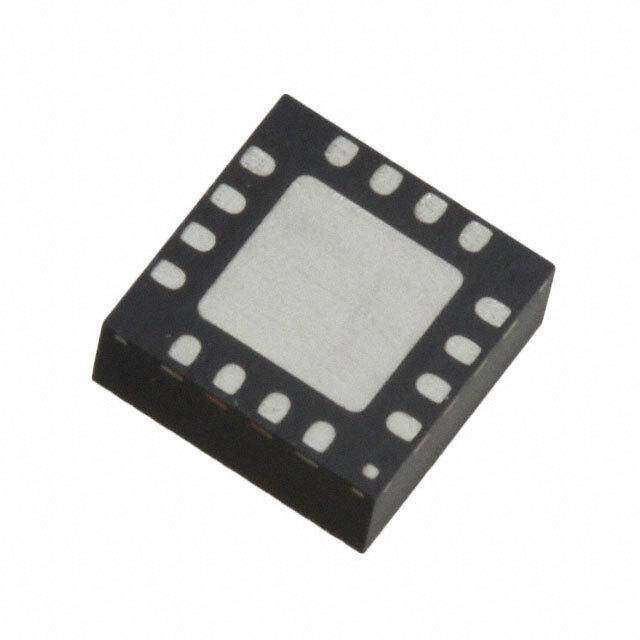
ICGOO电子元器件商城为您提供LIS331HH由STMicroelectronics设计生产,在icgoo商城现货销售,并且可以通过原厂、代理商等渠道进行代购。 LIS331HH价格参考¥36.57-¥36.57。STMicroelectronicsLIS331HH封装/规格:运动传感器 - 加速计, Accelerometer X, Y, Z Axis ±6g, 12g, 24g 25Hz ~ 500Hz 16-LGA (3x3)。您可以下载LIS331HH参考资料、Datasheet数据手册功能说明书,资料中有LIS331HH 详细功能的应用电路图电压和使用方法及教程。
| 参数 | 数值 |
| 产品目录 | |
| 描述 | IC ACCELEROMETER 3 AXIS 16LGA加速计 MEMS Digital Sensor 3-axes Nano |
| 产品分类 | 加速计运动与定位传感器 |
| 品牌 | STMicroelectronics |
| 产品手册 | |
| 产品图片 |
|
| rohs | 符合RoHS无铅 / 符合限制有害物质指令(RoHS)规范要求 |
| 产品系列 | 加速计,STMicroelectronics LIS331HHMEMS,纳米 |
| mouser_ship_limit | 根据美国政府的出口法规规定,Mouser无法将此产品销售到您所在的国家。 |
| 数据手册 | |
| 产品型号 | LIS331HH |
| 产品目录页面 | |
| 产品种类 | 加速计 |
| 传感轴 | X, Y, Z |
| 供应商器件封装 | 16-LGA(3x3) |
| 其它名称 | 497-10134 |
| 其它有关文件 | http://www.st.com/web/catalog/sense_power/FM89/SC444/PF247976?referrer=70071840 |
| 分辨率 | 16 bit |
| 加速 | 6 g, 12 g, 24 g |
| 加速度范围 | ±6g, 12g, 24g |
| 商标 | STMicroelectronics |
| 安装类型 | 表面贴装 |
| 封装 | Tray |
| 封装/外壳 | 16-VFLGA |
| 封装/箱体 | LGA-16 |
| 工厂包装数量 | 490 |
| 带宽 | 50Hz ~ 1kHz 可选 |
| 接口 | I2C, SPI |
| 数字输出-位数 | 16 bit |
| 数字输出-总线接口 | I2C, SPI |
| 最大工作温度 | + 85 C |
| 最小工作温度 | - 40 C |
| 标准包装 | 490 |
| 灵敏度 | 3 mg/digit, 6 mf/digit, 12 mg/digit |
| 特色产品 | http://www.digikey.com/cn/zh/ph/ST/LIS331.html |
| 电压-电源 | 2.16 V ~ 3.6 V |
| 电源电压-最大 | 3.6 V |
| 电源电压-最小 | 2.16 V |
| 电源电流 | 10 uA |
| 系列 | LIS331HH |
| 视频文件 | http://www.digikey.cn/classic/video.aspx?PlayerID=1364138032001&width=640&height=455&videoID=61455073001 |
| 轴 | X,Y,Z |
| 输出类型 | Digital |





- 商务部:美国ITC正式对集成电路等产品启动337调查
- 曝三星4nm工艺存在良率问题 高通将骁龙8 Gen1或转产台积电
- 太阳诱电将投资9.5亿元在常州建新厂生产MLCC 预计2023年完工
- 英特尔发布欧洲新工厂建设计划 深化IDM 2.0 战略
- 台积电先进制程称霸业界 有大客户加持明年业绩稳了
- 达到5530亿美元!SIA预计今年全球半导体销售额将创下新高
- 英特尔拟将自动驾驶子公司Mobileye上市 估值或超500亿美元
- 三星加码芯片和SET,合并消费电子和移动部门,撤换高东真等 CEO
- 三星电子宣布重大人事变动 还合并消费电子和移动部门
- 海关总署:前11个月进口集成电路产品价值2.52万亿元 增长14.8%




PDF Datasheet 数据手册内容提取
LIS331HH MEMS digital output motion sensor ultra low-power high full-scale 3-axes “nano” accelerometer Preliminary data Features ■ Wide supply voltage, 2.16 V to 3.6 V ■ Low voltage compatible IOs, 1.8 V ■ Ultra low-current mode consumption down to 10 µA ■ ±6g/±12g/±24g dynamically selectable full- LGA16 (3x3x1 mm) scale ■ I2C/SPI digital output interface accelerometer belonging to the “nano” family, with ■ 16 bit data output digital I2C/SPI serial interface standard output. ■ 2 independent programmable interrupt engines The device features ultra low-power operational modes that allow advanced power saving and ■ Sleep to wake-up function smart sleep to wake-up functions. ■ 6D orientation detection The LIS331HH has dynamically user selectable ■ Embedded self-test full scales of ±6g/±12g/±24g and it is capable of ■ 10000 g high shock survivability measuring accelerations with output data rates ■ ECOPACK® RoHS and “Green” compliant (see from 0.5 Hz to 1 kHz. The self-test capability Section8) allows the user to check the functioning of the sensor in the final application. Applications The device contains 2 indipendent interrupt engines able to recognize dedicated inertial ■ Pedometer events. ■ Gaming and virtual reality input devices Thresholds and timing of interrupt generators are programmable by the end user on the fly. ■ Motion activated functions ■ Impact recognition and logging The LIS331HH is available in small thin plastic land grid array package (LGA) and it is ■ Intelligent power saving for handheld devices guaranteed to operate over an extended ■ Vibration monitoring and compensation temperature range from -40 °C to +85 °C. Description The LIS331HH is an ultra low-power high performance high full-scale three axes linear Table 1. Device summary Order codes Temperature range [°C] Package Packaging LIS331HH -40 to +85 LGA16 Tray LIS331HHTR -40 to +85 LGA16 Tape and reel October 2009 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 1/37 This is preliminary information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to www.st.com 37 change without notice.
Contents LIS331HH Contents 1 Block diagram and pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 1.1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 1.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 2 Mechanical and electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 2.1 Mechanical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 2.2 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 2.3 Communication interface characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 2.3.1 SPI - serial peripheral interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 2.3.2 I2C - inter IC control interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 2.4 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 2.5 Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 2.5.1 Sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 2.5.2 Zero-g level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 2.5.3 Self-test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 2.5.4 Sleep to wake-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 3 Functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3.1 Sensing element . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3.2 IC interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3.3 Factory calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 4 Application hints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 4.1 Soldering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 5 Digital interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 5.1 I2C serial interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 5.1.1 I2C operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 5.2 SPI bus interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 5.2.1 SPI read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 5.2.2 SPI write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 5.2.3 SPI read in 3-wires mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 2/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Contents 6 Register mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 7 Register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 7.1 CTRL_REG1 (20h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 7.2 CTRL_REG2 (21h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 7.3 CTRL_REG3 [Interrupt CTRL register] (22h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 7.4 CTRL_REG4 (23h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 7.5 CTRL_REG5 (24h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 7.6 HP_FILTER_RESET (25h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 7.7 REFERENCE (26h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 7.8 STATUS_REG (27h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 7.9 OUT_X_L (28h), OUT_X_H (29) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 7.10 OUT_Y_L (2Ah), OUT_Y_H (2Bh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 7.11 OUT_Z_L (2Ch), OUT_Z_H (2Dh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 7.12 INT1_CFG (30h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 7.13 INT1_SRC (31h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 7.14 INT1_THS (32h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 7.15 INT1_DURATION (33h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 7.16 INT2_CFG (34h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 7.17 INT2_SRC (35h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33 7.18 INT2_THS (36h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 7.19 INT2_DURATION (37h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 8 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 9 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 3/37
List of tables LIS331HH List of tables Table 1. Device summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Table 3. Mechanical characteristics @ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted . . . . . . . . . . 9 Table 4. Electrical characteristics @ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Table 5. SPI slave timing values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Table 6. I2C slave timing values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Table 7. Absolute maximum ratings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 Table 8. Serial interface pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Table 9. Serial interface pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Table 10. SAD+Read/Write patterns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 Table 11. Transfer when master is writing one byte to slave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 Table 12. Transfer when master is writing multiple bytes to slave:. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Table 13. Transfer when master is receiving (reading) one byte of data from slave:. . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Table 14. Transfer when Master is receiving (reading) multiple bytes of data from slave . . . . . . . . . 19 Table 15. Register address map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 Table 16. CTRL_REG1 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 Table 17. CTRL_REG1 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 Table 18. Power mode and low-power output data rate configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 Table 19. Normal-mode output data rate configurations and low-pass cut-off frequencies . . . . . . . . 25 Table 20. CTRL_REG2 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 Table 21. CTRL_REG2 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 Table 22. High-pass filter mode configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Table 23. High-pass filter cut-off frequency configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Table 24. CTRL_REG3 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Table 25. CTRL_REG3 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Table 26. Data signal on INT 1 and INT 2 pad. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Table 27. CTRL_REG4 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Table 28. CTRL_REG4 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Table 29. CTRL_REG5 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 Table 30. CTRL_REG5 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 Table 31. Sleep to wake configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 Table 32. REFERENCE register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 Table 33. REFERENCE description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 Table 34. STATUS_REG register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 Table 35. STATUS_REG description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 Table 36. INT1_CFG register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 Table 37. INT1_CFG description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 Table 38. Interrupt 1 source configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Table 39. INT1_SRC register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Table 40. INT1_SRC description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Table 41. INT1_THS register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Table 42. INT1_THS description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 Table 43. INT1_DURATION register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 Table 44. INT2_DURATION description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 Table 45. INT2_CFG register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 Table 46. INT2_CFG description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 Table 47. Interrupt mode configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33 Table 48. INT2_SRC register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33 4/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH List of tables Table 49. INT2_SRC description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33 Table 50. INT2_THS register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 Table 51. INT2_THS description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 Table 52. INT2_DURATION register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 Table 53. INT2_DURATION description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 Table 54. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 5/37
List of figures LIS331HH List of figures Figure 1. Block diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Figure 2. Pin connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Figure 3. SPI slave timing diagram (2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Figure 4. I2C slave timing diagram (3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Figure 5. LIS331HH electrical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 Figure 6. Read and write protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 Figure 7. SPI read protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 Figure 8. Multiple bytes SPI read protocol (2 bytes example). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 Figure 9. SPI write protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 Figure 10. Multiple bytes SPI write protocol (2 bytes example). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Figure 11. SPI read protocol in 3-wires mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Figure 12. LGA16: Mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 6/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Block diagram and pin description 1 Block diagram and pin description 1.1 Block diagram Figure 1. Block diagram X+ Y+ CHARGE Z+ AMPLIFIER CS a A/D I2C SCL/SPC MUX CONVERTER CONTROL LOGIC SDA/SDO/SDI Z- SPI SDO/SA0 Y- X- TRIMMING CONTROL LOGIC INT 1 SELF TEST REFERENCE CIRCUITS CLOCK & INTERRUPT GEN. INT 2 1.2 Pin description Figure 2. Pin connection Z Pin 1 indicator 1 X 13 1 9 5 Y (TOP VIEW) (BOTTOM VIEW) DIRECTION OF THE DETECTABLE ACCELERATIONS Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 7/37
Block diagram and pin description LIS331HH T able 2. Pin description Pin# Name Function 1 Vdd_IO Power supply for I/O pins 2 NC Not connected 3 NC Not connected SCL I2C serial clock (SCL) 4 SPC SPI serial port clock (SPC) 5 GND 0V supply SDA I2C serial data (SDA) 6 SDI SPI serial data input (SDI) SDO 3-wire interface serial data output (SDO) SDO SPI serial data output (SDO) 7 SA0 I2C less significant bit of the device address (SA0) SPI enable 8 CS I2C/SPI mode selection (1: I2C mode; 0: SPI enabled) 9 INT 2 Inertial interrupt 2 10 Reserved Connect to GND 11 INT 1 Inertial interrupt 1 12 GND 0 V supply 13 GND 0 V supply 14 Vdd Power supply 15 Reserved Connect to Vdd 16 GND 0 V supply 8/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Mechanical and electrical specifications 2 Mechanical and electrical specifications 2.1 Mechanical characteristics Table 3. Mechanical characteristics @ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted (1) Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ.(2) Max. Unit FS bit set to 00 ±6 FS Measurement range(3) FS bit set to 01 ±12 g FS bit set to 11 ±24 FS bit set to 00 3 12 bit representation FS bit set to 01 So Sensitivity 6 mg/digit 12 bit representation FS bit set to 11 12 12 bit representation Sensitivity change vs TCSo FS bit set to 00 ±0.01 %/°C temperature Typical zero-g level offset TyOff FS bit set to 00 ±70 mg accuracy(4),(5) Zero-g level change vs TCOff Max delta from 25 °C ±0.4 mg/°C temperature An Acceleration noise density FS bit set to 00 650 µg/ Hz FS bit set to 00 50 110 180 LSb X axis Self-test FS bit set to 00 Vst -50 -100 -180 LSb output change(6),(7),(8) Y axis FS bit set to 00 220 290 370 LSb Z axis Top Operating temperature range -40 +85 °C Wh Product weight 20 mgram 1. The product is factory calibrated at 2.5 V. The operational power supply range is from 2.16 V to 3.6 V. 2. Typical specifications are not guaranteed 3. Verified by wafer level test and measurement of initial offset and sensitivity 4. Typical zero-g level offset value after MSL3 preconditioning 5. Offset can be eliminated by enabling the built-in high pass filter 6. The sign of “Self-test output change” is defined by CTRL_REG4 STsign bit (Table27), for all axes. 7. Self-test output changes with the power supply. “Self-test output change” is defined as OUTPUT[LSb] - OUTPUT[LSb] . 1LSb=12g/4096 at 12bit representation, ±6 g Full- (CTRL_REG4 ST bit=1) (CTRL_REG4 ST bit=0) scale 8. Output data reach 99% of final value after 1/ODR+1ms when enabling self-test mode, due to device filtering Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 9/37
Mechanical and electrical specifications LIS331HH 2.2 Electrical characteristics Table 4. Electrical characteristics @ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted (1) Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ.(2) Max. Unit Vdd Supply voltage 2.16 2.5 3.6 V Vdd_IO I/O pins supply voltage(3) 1.71 Vdd+0.1 V Current consumption Idd 250 µA in normal mode Current consumption IddLP 10 µA in low-power mode Current consumption in IddPdn 1 µA power-down mode Digital high level input VIH 0.8*Vdd_IO V voltage VIL Digital low level input voltage 0.2*Vdd_IO V VOH High level output voltage 0.9*Vdd_IO V VOL Low level output voltage 0.1*Vdd_IO V DR bit set to 00 50 DR bit set to 01 100 Output data rate ODR Hz in normal mode DR bit set to 10 400 DR bit set to 11 1000 PM bit set to 010 0.5 PM bit set to 011 1 Output data rate ODR PM bit set to 100 2 Hz LP in low-power mode PM bit set to 101 5 PM bit set to 110 10 BW System bandwidth(4) ODR/2 Hz Ton Turn-on time(5) ODR = 100 Hz 1/ODR+1ms s Top Operating temperature range -40 +85 °C 1. The product is factory calibrated at 2.5 V. The operational power supply range is from 2.16 V to 3.6 V. 2. Typical specification are not guaranteed 3. It is possible to remove Vdd maintaining Vdd_IO without blocking the communication busses, in this condition the measurement chain is powered off. 4. Refer to Table19 for filter cut-off frequency 5. Time to obtain valid data after exiting power-down mode 10/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Mechanical and electrical specifications 2.3 Communication interface characteristics 2.3.1 SPI - serial peripheral interface Subject to general operating conditions for Vdd and Top. Table 5. S PI slave timing values Value (1) Symbol Parameter Unit Min Max tc(SPC) SPI clock cycle 100 ns fc(SPC) SPI clock frequency 10 MHz tsu(CS) CS setup time 6 th(CS) CS hold time 8 tsu(SI) SDI input setup time 5 th(SI) SDI input hold time 15 ns tv(SO) SDO valid output time 50 th(SO) SDO output hold time 9 tdis(SO) SDO output disable time 50 Figure 3. SPI slave timing diagram (2) CS (3) (3) tsu(CS) tc(SPC) th(CS) SPC (3) (3) t t su(SI) h(SI) SDI (3) MSB IN LSB IN (3) tv(SO) th(SO) tdis(SO) SDO (3) MSB OUT LSB OUT (3) 1. Values are guaranteed at 10 MHz clock frequency for SPI with both 4 and 3 wires, based on characterization results, not tested in production 2. Measurement points are done at 0.2·Vdd_IO and 0.8·Vdd_IO, for both Input and output port 3. When no communication is on-going, data on CS, SPC, SDI and SDO are driven by internal pull-up resistors Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 11/37
Mechanical and electrical specifications LIS331HH 2.3.2 I2C - inter IC control interface Subject to general operating conditions for Vdd and Top. Table 6. I 2 C slave timing values I2C standard mode (1) I2C fast mode (1) Symbol Parameter Unit Min Max Min Max f(SCL) SCL clock frequency 0 100 0 400 KHz tw(SCLL) SCL clock low time 4.7 1.3 µs tw(SCLH) SCL clock high time 4.0 0.6 tsu(SDA) SDA setup time 250 100 ns th(SDA) SDA data hold time 0 3.45 0.01 0.9 µs tr(SDA) tr(SCL) SDA and SCL rise time 1000 20 + 0.1Cb (2) 300 ns tf(SDA) tf(SCL) SDA and SCL fall time 300 20 + 0.1Cb (2) 300 th(ST) START condition hold time 4 0.6 Repeated START condition tsu(SR) setup time 4.7 0.6 µs tsu(SP) STOP condition setup time 4 0.6 Bus free time between STOP tw(SP:SR) and START condition 4.7 1.3 Figure 4. I2C slave timing diagram (3) REPEATED START START t su(SR) t START SDA w(SP:SR) tf(SDA) tr(SDA) tsu(SDA) th(SDA) t STOP su(SP) SCL t t t t t h(ST) w(SCLL) w(SCLH) r(SCL) f(SCL) 1. Data based on standard I2C protocol requirement, not tested in production 2. Cb = total capacitance of one bus line, in pF 3. Measurement points are done at 0.2·Vdd_IO and 0.8·Vdd_IO, for both port 12/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Mechanical and electrical specifications 2.4 Absolute maximum ratings Stresses above those listed as “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device under these conditions is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. T able 7. Absolute maximum ratings Symbol Ratings Maximum value Unit Vdd Supply voltage -0.3 to 6 V Vdd_IO I/O pins Supply voltage -0.3 to 6 V Input voltage on any control pin Vin -0.3 to Vdd_IO +0.3 V (CS, SCL/SPC, SDA/SDI/SDO, SDO/SA0) 3000 g for 0.5 ms A Acceleration (any axis, powered, Vdd = 2.5 V) POW 10000 g for 0.1 ms 3000 g for 0.5 ms A Acceleration (any axis, unpowered) UNP 10000 g for 0.1 ms T Operating temperature range -40 to +85 °C OP T Storage temperature range -40 to +125 °C STG 4 (HBM) kV ESD Electrostatic discharge protection 1.5 (CDM) kV 200 (MM) V Note: Supply voltage on any pin should never exceed 6.0 V This is a mechanical shock sensitive device, improper handling can cause permanent damages to the part This is an ESD sensitive device, improper handling can cause permanent damages to the part Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 13/37
Mechanical and electrical specifications LIS331HH 2.5 Terminology 2.5.1 Sensitivity Sensitivity describes the gain of the sensor and can be determined e.g. by applying 1 g acceleration to it. As the sensor can measure DC accelerations this can be done easily by pointing the axis of interest towards the center of the earth, noting the output value, rotating the sensor by 180 degrees (pointing to the sky) and noting the output value again. By doing so, ±1 g acceleration is applied to the sensor. Subtracting the larger output value from the smaller one, and dividing the result by 2, leads to the actual sensitivity of the sensor. This value changes very little over temperature and also time. The sensitivity tolerance describes the range of Sensitivities of a large population of sensors. 2.5.2 Zero-g level Zero-g level offset (TyOff) describes the deviation of an actual output signal from the ideal output signal if no acceleration is present. A sensor in a steady state on a horizontal surface will measure 0 g in X axis and 0 g in Y axis whereas the Z axis will measure 1 g. The output is ideally in the middle of the dynamic range of the sensor (content of OUT registers 00h, data expressed as 2’s complement number). A deviation from ideal value in this case is called Zero-g offset. Offset is to some extent a result of stress to MEMS sensor and therefore the offset can slightly change after mounting the sensor onto a printed circuit board or exposing it to extensive mechanical stress. Offset changes little over temperature, see “Zero-g level change vs. temperature”. The Zero-g level tolerance (TyOff) describes the standard deviation of the range of Zero-g levels of a population of sensors. 2.5.3 Self-test Self-test allows to check the sensor functionality without moving it. The self-test function is off when the self-test bit (ST) of CTRL_REG4 (control register 4) is programmed to ‘0‘. When the self-test bit of CTRL_REG4 is programmed to ‘1‘ an actuation force is applied to the sensor, simulating a definite input acceleration. In this case the sensor outputs will exhibit a change in their DC levels which are related to the selected full scale through the device sensitivity. When self-test is activated, the device output level is given by the algebraic sum of the signals produced by the acceleration acting on the sensor and by the electrostatic test-force. If the output signals change within the amplitude specified inside Table3, then the sensor is working properly and the parameters of the interface chip are within the defined specifications. 2.5.4 Sleep to wake-up The “sleep to wake-up” function, in conjunction with low-power mode, allows to further reduce the system power consumption and develop new smart applications. LIS331HH may be set in a low-power operating mode, characterized by lower date rates refreshments. In this way the device, even if sleeping, keep on sensing acceleration and generating interrupt requests. When the “sleep to wake-up” function is activated, LIS331HH is able to automatically wake- up as soon as the interrupt event has been detected, increasing the output data rate and bandwidth. With this feature the system may be efficiently switched from low-power mode to full- performance depending on user-selectable positioning and acceleration events, thus ensuring power saving and flexibility. 14/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Functionality 3 Functionality The LIS331HH is a “nano”, low-power, high full-scale digital output 3-axis linear accelerometer packaged in a LGA package. The complete device includes a sensing element and an IC interface able to take the information from the sensing element and to provide a signal to the external world through an I2C/SPI serial interface. 3.1 Sensing element A proprietary process is used to create a surface micro-machined accelerometer. The technology allows to carry out suspended silicon structures which are attached to the substrate in a few points called anchors and are free to move in the direction of the sensed acceleration. To be compatible with the traditional packaging techniques a cap is placed on top of the sensing element to avoid blocking the moving parts during the moulding phase of the plastic encapsulation. When an acceleration is applied to the sensor the proof mass displaces from its nominal position, causing an imbalance in the capacitive half-bridge. This imbalance is measured using charge integration in response to a voltage pulse applied to the capacitor. At steady state the nominal value of the capacitors are few pF and when an acceleration is applied the maximum variation of the capacitive load is in the fF range. 3.2 IC interface The complete measurement chain is composed by a low-noise capacitive amplifier which converts the capacitive unbalancing of the MEMS sensor into an analog voltage that is finally available to the user by an analog-to-digital converter. The acceleration data may be accessed through an I2C/SPI interface thus making the device particularly suitable for direct interfacing with a microcontroller. The LIS331HH features a Data-Ready signal (RDY) which indicates when a new set of measured acceleration data is available thus simplifying data synchronization in the digital system that uses the device. The LIS331HH may also be configured to generate an inertial dedicated interrupt signals accordingly to a programmed acceleration event along the enabled axes. Both interrupt can be available simultaneously on two different pins. 3.3 Factory calibration The IC interface is factory calibrated for sensitivity (So) and Zero-g level (TyOff). The trimming values are stored inside the device in a non volatile memory. Any time the device is turned on, the trimming parameters are downloaded into the registers to be used during the active operation. This allows to use the device without further calibration. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 15/37
Application hints LIS331HH 4 Application hints Figure 5. LIS331HH electrical connection Vdd 16 14 10µF Vdd_IO 1 13 TOP VIEW INT 1 100nF 55 99 6 8 INT 2 O D SCL/SPC SDA/SDI/S SDO/SA0 CS GND Digital signal from/to signal controller.Signal’s levels are defined by proper selection of Vdd_IO The device core is supplied through Vdd line while the I/O pads are supplied through Vdd_IO line. Power supply decoupling capacitors (100 nF ceramic, 10 µF Aluminum) should be placed as near as possible to the pin 14 of the device (common design practice). All the voltage and ground supplies must be present at the same time to have proper behavior of the IC (refer to Figure5). It is possible to remove Vdd maintaining Vdd_IO without blocking the communication bus, in this condition the measurement chain is powered off. The functionality of the device and the measured acceleration data is selectable and accessible through the I2C or SPI interfaces.When using the I2C, CS must be tied high. The functions, the threshold and the timing of the two interrupt pins (INT 1 and INT 2) can be completely programmed by the user through the I2C/SPI interface. 4.1 Soldering information The LGA package is compliant with the ECOPACK®, RoHS and “Green” standard. It is qualified for soldering heat resistance according to JEDEC J-STD-020C. Leave “Pin 1 Indicator” unconnected during soldering. Land pattern and soldering recommendations are available at www.st.com. 16/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Digital interfaces 5 Digital interfaces The registers embedded inside the LIS331HH may be accessed through both the I2C and SPI serial interfaces. The latter may be SW configured to operate either in 3-wire or 4-wire interface mode. The serial interfaces are mapped onto the same pads. To select/exploit the I2C interface, CS line must be tied high (i.e. connected to Vdd_IO). T able 8. Serial interface pin description Pin name Pin description SPI enable CS I2C/SPI mode selection (1: I2C mode; 0: SPI enabled) SCL I2C serial clock (SCL) SPC SPI serial port clock (SPC) SDA I2C serial data (SDA) SDI SPI serial data input (SDI) SDO 3-wire interface serial data output (SDO) SA0 I2C less significant bit of the device address (SA0) SDO SPI serial data output (SDO) 2 5.1 I C serial interface The LIS331HH I2C is a bus slave. The I2C is employed to write data into registers whose content can also be read back. The relevant I2C terminology is given in the table below. T able 9. Serial interface pin description Term Description Transmitter The device which sends data to the bus Receiver The device which receives data from the bus The device which initiates a transfer, generates clock signals and terminates a Master transfer Slave The device addressed by the master There are two signals associated with the I2C bus: the serial clock line (SCL) and the Serial DAta line (SDA). The latter is a bidirectional line used for sending and receiving the data to/from the interface. Both the lines are connected to Vdd_IO through a pull-up resistor embedded inside the LIS331HH. When the bus is free both the lines are high. The I2C interface is compliant with fast mode (400 kHz) I2C standards as well as with the normal mode. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 17/37
Digital interfaces LIS331HH 5.1.1 I2C operation The transaction on the bus is started through a START (ST) signal. A START condition is defined as a HIGH to LOW transition on the data line while the SCL line is held HIGH. After this has been transmitted by the Master, the bus is considered busy. The next byte of data transmitted after the start condition contains the address of the slave in the first 7 bits and the eighth bit tells whether the Master is receiving data from the slave or transmitting data to the slave. When an address is sent, each device in the system compares the first seven bits after a start condition with its address. If they match, the device considers itself addressed by the Master. The Slave ADdress (SAD) associated to the LIS331HH is 001100xb. SDO/SA0 pad can be used to modify less significant bit of the device address. If SA0 pad is connected to voltage supply, LSb is ‘1’ (address 0011001b) else if SA0 pad is connected to ground, LSb value is ‘0’ (address 0011000b). This solution permits to connect and address two different accelerometers to the same I2C lines. Data transfer with acknowledge is mandatory. The transmitter must release the SDA line during the acknowledge pulse. The receiver must then pull the data line LOW so that it remains stable low during the HIGH period of the acknowledge clock pulse. A receiver which has been addressed is obliged to generate an acknowledge after each byte of data received. The I2C embedded inside the LIS331HH behaves like a slave device and the following protocol must be adhered to. After the start condition (ST) a slave address is sent, once a slave acknowledge (SAK) has been returned, a 8-bit sub-address (SUB) is transmitted: the 7 LSb represent the actual register address while the MSB enables address auto increment. If the MSb of the SUB field is ‘1’, the SUB (register address) is automatically increased to allow multiple data read/write. The slave address is completed with a Read/Write bit. If the bit was ‘1’ (Read), a repeated START (SR) condition must be issued after the two sub-address bytes; if the bit is ‘0’ (Write) the Master will transmit to the slave with direction unchanged. Table10 explains how the SAD+Read/Write bit pattern is composed, listing all the possible configurations. Table 10. SAD+Read/Write patterns Command SAD[6:1] SAD[0] = SA0 R/W SAD+R/W Read 001100 0 1 00110001 (31h) Write 001100 0 0 00110000 (30h) Read 001100 1 1 00110011 (33h) Write 001100 1 0 00110010 (32h) Table 11. Transfer when master is writing one byte to slave Master ST SAD + W SUB DATA SP Slave SAK SAK SAK 18/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Digital interfaces Table 12. Transfer when master is writing multiple bytes to slave: Master ST SAD + W SUB DATA DATA SP Slave SAK SAK SAK SAK Table 13. Transfer when master is receiving (reading) one byte of data from slave: Master ST SAD + W SUB SR SAD + R NMAK SP Slave SAK SAK SAK DATA Table 14. Transfer when Master is receiving (reading) multiple bytes of data from slave Master ST SAD+W SUB SR SAD+R MAK MAK NMAK SP Slave SAK SAK SAK DATA DATA DATA Data are transmitted in byte format (DATA). Each data transfer contains 8 bits. The number of bytes transferred per transfer is unlimited. Data is transferred with the Most Significant bit (MSb) first. If a receiver can’t receive another complete byte of data until it has performed some other function, it can hold the clock line, SCL LOW to force the transmitter into a wait state. Data transfer only continues when the receiver is ready for another byte and releases the data line. If a slave receiver doesn’t acknowledge the slave address (i.e. it is not able to receive because it is performing some real time function) the data line must be left HIGH by the slave. The Master can then abort the transfer. A LOW to HIGH transition on the SDA line while the SCL line is HIGH is defined as a STOP condition. Each data transfer must be terminated by the generation of a STOP (SP) condition. In order to read multiple bytes, it is necessary to assert the most significant bit of the sub- address field. In other words, SUB(7) must be equal to 1 while SUB(6-0) represents the address of first register to be read. In the presented communication format MAK is Master acknowledge and NMAK is No Master Acknowledge. 5.2 SPI bus interface The LIS331HH SPI is a bus slave. The SPI allows to write and read the registers of the device. The Serial Interface interacts with the outside world with 4 wires: CS, SPC, SDI and SDO. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 19/37
Digital interfaces LIS331HH Figure 6. Read and write protocol CS SPC SDI RW DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0 MS AD5 AD4AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0 SDO DO7DO6DO5DO4DO3DO2DO1DO0 CS is the serial port enable and it is controlled by the SPI master. It goes low at the start of the transmission and goes back high at the end. SPC is the serial port clock and it is controlled by the SPI master. It is stopped high when CS is high (no transmission). SDI and SDO are respectively the serial port data input and output. Those lines are driven at the falling edge of SPC and should be captured at the rising edge of SPC. Both the read register and write register commands are completed in 16 clock pulses or in multiple of 8 in case of multiple bytes read/write. Bit duration is the time between two falling edges of SPC. The first bit (bit 0) starts at the first falling edge of SPC after the falling edge of CS while the last bit (bit 15, bit 23, ...) starts at the last falling edge of SPC just before the rising edge of CS. bit 0: RW bit. When 0, the data DI(7:0) is written into the device. When 1, the data DO(7:0) from the device is read. In latter case, the chip will drive SDO at the start of bit 8. bit 1: MS bit. When 0, the address will remain unchanged in multiple read/write commands. When 1, the address is auto incremented in multiple read/write commands. bit 2-7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register. bit 8-15: data DI(7:0) (write mode). This is the data that is written into the device (MSb first). bit 8-15: data DO(7:0) (read mode). This is the data that is read from the device (MSb first). In multiple read/write commands further blocks of 8 clock periods will be added. When MS bit is ‘0’ the address used to read/write data remains the same for every block. When MS bit is ‘1’ the address used to read/write data is increased at every block. The function and the behavior of SDI and SDO remain unchanged. 5.2.1 SPI read Figure 7. SPI read protocol CS SPC SDI RW MSAD5AD4AD3AD2AD1AD0 SDO DO7DO6DO5DO4DO3DO2DO1DO0 20/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Digital interfaces The SPI Read command is performed with 16 clock pulses. Multiple byte read command is performed adding blocks of 8 clock pulses at the previous one. bit 0: READ bit. The value is 1. bit 1: MS bit. When 0 do not increment address, when 1 increment address in multiple reading. bit 2-7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register. bit 8-15: data DO(7:0) (read mode). This is the data that will be read from the device (MSb first). bit 16-... : data DO(...-8). Further data in multiple byte reading. Figure 8. Multiple bytes SPI read protocol (2 bytes example) CS SPC SDI RW MS AD5AD4AD3AD2AD1AD0 SDO DO7DO6DO5DO4DO3DO2DO1DO0DO15D O14D O13D O12D O11D O10D O9DO8 5.2.2 SPI write Figure 9. SPI write protocol CS SPC SDI RW DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0 MS AD5 AD4AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0 The SPI Write command is performed with 16 clock pulses. Multiple byte write command is performed adding blocks of 8 clock pulses at the previous one. bit 0: WRITE bit. The value is 0. bit 1: MS bit. When 0 do not increment address, when 1 increment address in multiple writing. bit 2 -7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register. bit 8-15: data DI(7:0) (write mode). This is the data that will be written inside the device (MSb first). bit 16-... : data DI(...-8). Further data in multiple byte writing. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 21/37
Digital interfaces LIS331HH Figure 10. Multiple bytes SPI write protocol (2 bytes example) CS SPC SDI DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0 DI15 DI14 DI13 DI12 DI11 DI10 DI9 DI8 RW MSAD5AD4AD3AD2AD1AD0 5.2.3 SPI read in 3-wires mode 3-wires mode is entered by setting to ‘1’ bit SIM (SPI serial interface mode selection) in CTRL_REG4. Figure 11. SPI read protocol in 3-wires mode CS SPC SDI/O RW DO7 DO6 DO5 DO4 DO3 DO2 DO1 DO0 MS AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0 The SPI read command is performed with 16 clock pulses: bit 0: READ bit. The value is 1. bit 1: MS bit. When 0 do not increment address, when 1 increment address in multiple reading. bit 2-7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register. bit 8-15: data DO(7:0) (read mode). This is the data that is read from the device (MSb first). Multiple read command is also available in 3-wires mode. 22/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Register mapping 6 Register mapping The table given below provides a listing of the 8 bit registers embedded in the device and the related addresses: T able 15. Register address map Register address Name Type Default Comment Hex Binary Reserved (do not modify) 00 - 1F Reserved CTRL_REG1 rw 20 010 0000 00000111 CTRL_REG2 rw 21 010 0001 00000000 CTRL_REG3 rw 22 010 0010 00000000 CTRL_REG4 rw 23 010 0011 00000000 CTRL_REG5 rw 24 010 0100 00000000 HP_FILTER_RESET r 25 010 0101 Dummy register REFERENCE rw 26 010 0110 00000000 STATUS_REG r 27 010 0111 00000000 OUT_X_L r 28 010 1000 output OUT_X_H r 29 010 1001 output OUT_Y_L r 2A 010 1010 output OUT_Y_H r 2B 010 1011 output OUT_Z_L r 2C 010 1100 output OUT_Z_H r 2D 010 1101 output Reserved (do not modify) 2E - 2F Reserved INT1_CFG rw 30 011 0000 00000000 INT1_SOURCE r 31 011 0001 00000000 INT1_THS rw 32 011 0010 00000000 INT1_DURATION rw 33 011 0011 00000000 INT2_CFG rw 34 011 0100 00000000 INT2_SOURCE r 35 011 0101 00000000 INT2_THS rw 36 011 0110 00000000 INT2_DURATION rw 37 011 0111 00000000 Reserved (do not modify) 38 - 3F Reserved Registers marked as Reserved must not be changed. The writing to those registers may cause permanent damages to the device. The content of the registers that are loaded at boot should not be changed. They contain the factory calibration values. Their content is automatically restored when the device is powered-up. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 23/37
Register description LIS331HH 7 Register description The device contains a set of registers which are used to control its behavior and to retrieve acceleration data. The registers address, made of 7 bits, is used to identify them and to write the data through serial interface. 7.1 CTRL_REG1 (20h) Table 16. CTRL_REG1 register PM2 PM1 PM0 DR1 DR0 Zen Yen Xen Table 17. CTRL_REG1 description Power mode selection. Default value: 000 PM2 - PM0 (000: Power-down; Others: refer to Table18) Data rate selection. Default value: 00 DR1, DR0 (00:50 Hz; Others: refer to Table19) Z axis enable. Default value: 1 Zen (0: Z axis disabled; 1: Z axis enabled) Y axis enable. Default value: 1 Yen (0: Y axis disabled; 1: Y axis enabled) X axis enable. Default value: 1 Xen (0: X axis disabled; 1: X axis enabled) PM bits allow to select between power-down and two operating active modes. The device is in power-down mode when PD bits are set to “000” (default value after boot). Table18 shows all the possible power mode configurations and respective output data rates. Output data in the low-power modes are computed with low-pass filter cut-off frequency defined by DR1, DR0 bits. DR bits, in the normal-mode operation, select the data rate at which acceleration samples are produced. In low-power mode they define the output data resolution. Table19 shows all the possible configuration for DR1 and DR0 bits. Table 18. Power mode and low-power output data rate configurations Output data rate [Hz] PM2 PM1 PM0 Power mode selection ODR LP 0 0 0 Power-down -- 0 0 1 Normal mode ODR 0 1 0 Low-power 0.5 0 1 1 Low-power 1 1 0 0 Low-power 2 24/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Register description Table 18. Power mode and low-power output data rate configurations (continued) Output data rate [Hz] PM2 PM1 PM0 Power mode selection ODR LP 1 0 1 Low-power 5 1 1 0 Low-power 10 Table 19. Normal-mode output data rate configurations and low-pass cut-off frequencies Output Data Rate [Hz] Low-pass filter cut-off DR1 DR0 ODR frequency [Hz] 0 0 50 37 0 1 100 74 1 0 400 292 1 1 1000 780 7.2 CTRL_REG2 (21h) Table 20. CTRL_REG2 register BOOT HPM1 HPM0 FDS HPen2 HPen1 HPCF1 HPCF0 Table 21. CTRL_REG2 description Reboot memory content. Default value: 0 BOOT (0: normal mode; 1: reboot memory content) High pass filter mode selection. Default value: 00 HPM1, HPM0 (00: normal mode; Others: refer to Table22) Filtered data selection. Default value: 0 FDS (0: internal filter bypassed; 1: data from internal filter sent to output register) High pass filter enabled for interrupt 2 source. Default value: 0 HPen2 (0: filter bypassed; 1: filter enabled) High pass filter enabled for interrupt 1 source. Default value: 0 HPen1 (0: filter bypassed; 1: filter enabled) HPCF1, High pass filter cut-off frequency configuration. Default value: 00 HPCF0 (00: HPc=8; 01: HPc=16; 10: HPc=32; 11: HPc=64) BOOT bit is used to refresh the content of internal registers stored in the flash memory block. At the device power up the content of the flash memory block is transferred to the internal registers related to trimming functions to permit a good behavior of the device itself. If for any reason the content of trimming registers was changed it is sufficient to use this bit to restore correct values. When BOOT bit is set to ‘1’ the content of internal flash is copied Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 25/37
Register description LIS331HH inside corresponding internal registers and it is used to calibrate the device. These values are factory trimmed and they are different for every accelerometer. They permit a good behavior of the device and normally they have not to be changed. At the end of the boot process the BOOT bit is set again to ‘0’. Table 22. High-pass filter mode configuration HPM1 HPM0 High-pass filter mode 0 0 Normal mode (reset reading HP_RESET_FILTER) 0 1 Reference signal for filtering 1 0 Normal mode (reset reading HP_RESET_FILTER) HPCF[1:0]. These bits are used to configure high-pass filter cut-off frequency ft which is given by: ft = ln⎝⎛1–H-----1P-----c--⎠⎞ ⋅ 2--f--sπ-- The equation can be simplified to the following approximated equation: f f = ------------s---------- t 6⋅ HPc T able 23. High-pass filter cut-off frequency configuration f [Hz] f [Hz] f [Hz] f [Hz] t t t t HPcoeff2,1 Data rate = 50 Hz Data rate = 100 Hz Data rate = 400 Hz Data rate = 1000 Hz 00 1 2 8 20 01 0.5 1 4 10 10 0.25 0.5 2 5 11 0.125 0.25 1 2.5 7.3 CTRL_REG3 [Interrupt CTRL register] (22h) Table 24. CTRL_REG3 register IHL PP_OD LIR2 I2_CFG1 I2_CFG0 LIR1 I1_CFG1 I1_CFG0 Table 25. CTRL_REG3 description Interrupt active high, low. Default value: 0 IHL (0: active high; 1:active low) Push-pull/Open drain selection on interrupt pad. Default value 0. PP_OD (0: push-pull; 1: open drain) 26/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Register description Table 25. CTRL_REG3 description (continued) Latch interrupt request on INT2_SRC register, with INT2_SRC register cleared by LIR2 reading INT2_SRC itself. Default value: 0. (0: interrupt request not latched; 1: interrupt request latched) I2_CFG1, Data signal on INT 2 pad control bits. Default value: 00. I2_CFG0 (see table below) Latch interrupt request on INT1_SRC register, with INT1_SRC register cleared by LIR1 reading INT1_SRC register. Default value: 0. (0: interrupt request not latched; 1: interrupt request latched) I1_CFG1, Data signal on INT 1 pad control bits. Default value: 00. I1_CFG0 (see table below) Table 26. Data signal on INT 1 and INT 2 pad I1(2)_CFG1 I1(2)_CFG0 INT 1(2) Pad 0 0 Interrupt 1 (2) source 0 1 Interrupt 1 source OR interrupt 2 source 1 0 Data ready 1 1 Boot running 7.4 CTRL_REG4 (23h) Table 27. CTRL_REG4 register BDU BLE FS1 FS0 STsign 0 ST SIM Table 28. CTRL_REG4 description Block data update. Default value: 0 BDU (0: continuos update; 1: output registers not updated between MSB and LSB reading) Big/little endian data selection. Default value 0. BLE (0: data LSB @ lower address; 1: data MSB @ lower address) Full-scale selection. Default value: 00. FS1, FS0 (00: ±6 g; 01: ±12 g; 11: ±24 g) Self-test sign. Default value: 00. STsign (0: self-test plus; 1 self-test minus) Self-test enable. Default value: 0. ST (0: self-test disabled; 1: self-test enabled) SPI serial interface mode selection. Default value: 0. SIM (0: 4-wire interface; 1: 3-wire interface) Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 27/37
Register description LIS331HH BDU bit is used to inhibit output registers update between the reading of upper and lower register parts. In default mode (BDU = ‘0’) the lower and upper register parts are updated continuously. If it is not sure to read faster than output data rate, it is recommended to set BDU bit to ‘1’. In this way, after the reading of the lower (upper) register part, the content of that output registers is not updated until the upper (lower) part is read too. This feature avoids reading LSB and MSB related to different samples. 7.5 CTRL_REG5 (24h) Table 29. CTRL_REG5 register 0 0 0 0 0 0 TurnOn1 TurnOn0 Table 30. CTRL_REG5 description TurnOn1, Turn-on mode selection for sleep to wake function. Default value: 00. TurnOn0 TurnOn bits are used for turning on the sleep to wake function. Table 31. Sleep to wake configuration TurnOn1 TurnOn0 Sleep to wake status 0 0 Sleep to wake function is disabled Turned on: The device is in low power mode (ODR is defined in 1 1 CTRL_REG1) Setting TurnOn[1:0] bits to 11 the “sleep to wake” function is enabled. When an interrupt event occurs the device is turned to normal mode increasing the ODR to the value defined in CTRL_REG1. Although the device is in normal mode, CTRL_REG1 content is not automatically changed to “normal mode” configuration. 7.6 HP_FILTER_RESET (25h) Dummy register. Reading at this address zeroes instantaneously the content of the internal high pass-filter. If the high pass filter is enabled all three axes are instantaneously set to 0g. This allows to overcome the settling time of the high pass filter. 7.7 REFERENCE (26h) Table 32. REFERENCE register Ref7 Ref6 Ref5 Ref4 Ref3 Ref2 Ref1 Ref0 28/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Register description Table 33. REFERENCE description Ref7 - Ref0 Reference value for high-pass filter. Default value: 00h. This register sets the acceleration value taken as a reference for the high-pass filter output. When filter is turned on (at least one of FDS, HPen2, or HPen1 bit is equal to ‘1’) and HPM bits are set to “01”, filter out is generated taking this value as a reference. 7.8 STATUS_REG (27h) Table 34. STATUS_REG register ZYXOR ZOR YOR XOR ZYXDA ZDA YDA XDA Table 35. STATUS_REG description X, Y and Z axis data overrun. Default value: 0 ZYXOR (0: no overrun has occurred; 1: new data has overwritten the previous one before it was read) Z axis data overrun. Default value: 0 ZOR (0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the Z-axis has overwritten the previous one) Y axis data overrun. Default value: 0 YOR (0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the Y-axis has overwritten the previous one) X axis data overrun. Default value: 0 XOR (0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the X-axis has overwritten the previous one) ZYXDA X, Y and Z axis new data available. Default value: 0 (0: a new set of data is not yet available; 1: a new set of data is available) ZDA Z axis new data available. Default value: 0 (0: a new data for the Z-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the Z-axis is available) YDA Y axis new data available. Default value: 0 (0: a new data for the Y-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the Y-axis is available) XDA X axis new data available. Default value: 0 (0: a new data for the X-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the X-axis is available) 7.9 OUT_X_L (28h), OUT_X_H (29) X-axis acceleration data. The value is expressed as two’s complement. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 29/37
Register description LIS331HH 7.10 OUT_Y_L (2Ah), OUT_Y_H (2Bh) Y-axis acceleration data. The value is expressed as two’s complement. 7.11 OUT_Z_L (2Ch), OUT_Z_H (2Dh) Z-axis acceleration data. The value is expressed as two’s complement. 7.12 INT1_CFG (30h) Table 36. INT1_CFG register AOI 6D ZHIE ZLIE YHIE YLIE XHIE XLIE Table 37. INT1_CFG description AND/OR combination of Interrupt events. Default value: 0. AOI (See Table38) 6 direction detection function enable. Default value: 0. 6D (See Table38) Enable interrupt generation on Z high event. Default value: 0 ZHIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value higher than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on Z low event. Default value: 0 ZLIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value lower than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on Y high event. Default value: 0 YHIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value higher than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on Y low event. Default value: 0 YLIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value lower than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on X high event. Default value: 0 XHIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value higher than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on X low event. Default value: 0 XLIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value lower than preset threshold) Configuration register for Interrupt 1 source. 30/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Register description Table 38. Interrupt 1 source configurations AOI 6D Interrupt mode 0 0 OR combination of interrupt events 0 1 6 direction movement recognition 1 0 AND combination of interrupt events 1 1 6 direction position recognition 7.13 INT1_SRC (31h) Table 39. INT1_SRC register 0 IA ZH ZL YH YL XH XL Table 40. INT1_SRC description Interrupt active. Default value: 0 IA (0: no interrupt has been generated; 1: one or more interrupts have been generated) Z high. Default value: 0 ZH (0: no interrupt, 1: Z High event has occurred) Z low. Default value: 0 ZL (0: no interrupt; 1: Z Low event has occurred) Y high. Default value: 0 YH (0: no interrupt, 1: Y High event has occurred) Y low. Default value: 0 YL (0: no interrupt, 1: Y Low event has occurred) X high. Default value: 0 XH (0: no interrupt, 1: X High event has occurred) X low. Default value: 0 XL (0: no interrupt, 1: X Low event has occurred) Interrupt 1 source register. Read only register. Reading at this address clears INT1_SRC IA bit (and the interrupt signal on INT 1 pin) and allows the refreshment of data in the INT1_SRC register if the latched option was chosen. 7.14 INT1_THS (32h) Table 41. INT1_THS register 0 THS6 THS5 THS4 THS3 THS2 THS1 THS0 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 31/37
Register description LIS331HH Table 42. INT1_THS description THS6 - THS0 Interrupt 1 threshold. Default value: 000 0000 7.15 INT1_DURATION (33h) Table 43. INT1_DURATION register 0 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Table 44. INT2_DURATION description D6 - D0 Duration value. Default value: 000 0000 D6 - D0 bits set the minimum duration of the Interrupt 2 event to be recognized. Duration steps and maximum values depend on the ODR chosen. 7.16 INT2_CFG (34h) Table 45. INT2_CFG register AOI 6D ZHIE ZLIE YHIE YLIE XHIE XLIE Table 46. INT2_CFG description AND/OR combination of interrupt events. Default value: 0. AOI (See table below) 6 direction detection function enable. Default value: 0. 6D (See table below) Enable interrupt generation on Z high event. Default value: 0 ZHIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value higher than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on Z low event. Default value: 0 ZLIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value lower than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on Y high event. Default value: 0 YHIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value higher than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on Y low event. Default value: 0 YLIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value lower than preset threshold) 32/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Register description Table 46. INT2_CFG description Enable interrupt generation on X high event. Default value: 0 XHIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value higher than preset threshold) Enable interrupt generation on X low event. Default value: 0 XLIE (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value lower than preset threshold) Configuration register for Interrupt 2 source. Table 47. Interrupt mode configuration AOI 6D Interrupt mode 0 0 OR combination of interrupt events 0 1 6 direction movement recognition 1 0 AND combination of interrupt events 1 1 6 direction position recognition 7.17 INT2_SRC (35h) Table 48. INT2_SRC register 0 IA ZH ZL YH YL XH XL Table 49. INT2_SRC description Interrupt active. Default value: 0 IA (0: no interrupt has been generated; 1: one or more interrupts have been generated) Z high. Default value: 0 ZH (0: no interrupt, 1: Z high event has occurred) Z low. Default value: 0 ZL (0: no interrupt; 1: Z low event has occurred) Y high. Default value: 0 YH (0: no interrupt, 1: Y high event has occurred) Y low. Default value: 0 YL (0: no interrupt, 1: Y low event has occurred) X high. Default value: 0 XH (0: no interrupt, 1: X high event has occurred) X Low. Default value: 0 XL (0: no interrupt, 1: X low event has occurred) Interrupt 2 source register. Read only register. Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 33/37
Register description LIS331HH Reading at this address clears INT2_SRC IA bit (and the interrupt signal on INT 2 pin) and allows the refreshment of data in the INT2_SRC register if the latched option was chosen. 7.18 INT2_THS (36h) Table 50. INT2_THS register 0 THS6 THS5 THS4 THS3 THS2 THS1 THS0 Table 51. INT2_THS description THS6 - THS0 Interrupt 1 threshold. Default value: 000 0000 7.19 INT2_DURATION (37h) Table 52. INT2_DURATION register 0 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Table 53. INT2_DURATION description D6 - D0 Duration value. Default value: 000 0000 D6 - D0 bits set the minimum duration of the Interrupt 2 event to be recognized. Duration time steps and maximum values depend on the ODR chosen. 34/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Package information 8 Package information In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of ECOPACK® packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK® specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com. ECOPACK is an ST trademark. Figure 12. LGA16: Mechanical data and package dimensions Dimensions mm inch Outline and Ref. Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max. mechanical data A1 1.000 0.0394 A2 0.785 0.0309 A3 0.200 0.0079 D1 2.850 3.000 3.150 0.1122 0.1181 0.1240 E1 2.850 3.000 3.150 0.1122 0.1181 0.1240 L1 1.000 1.060 0.0394 0.0417 L2 2.000 2.060 0.0787 0.0811 N1 0.500 0.0197 N2 1.000 0.0394 M 0.040 0.100 0.160 0.0016 0.0039 0.0063 P1 0.875 0.0344 P2 1.275 0.0502 LGA16 (3x3x1.0mm) T1 0.290 0.350 0.410 0.0114 0.0138 0.0161 Land Grid Array Package T2 0.190 0.250 0.310 0.0075 0.0098 0.0122 d 0.150 0.0059 k 0.050 0.0020 7983231 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 35/37
Revision history LIS331HH 9 Revision history T able 54. Document revision history Date Revision Changes 05-Oct-2009 1 Initial release 36/37 Doc ID 16366 Rev 1
LIS331HH Please Read Carefully: Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notice. All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale. Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein. UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY, DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK. Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any liability of ST. ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries. Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners. © 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved STMicroelectronics group of companies Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America www.st.com Doc ID 16366 Rev 1 37/37
Mouser Electronics Authorized Distributor Click to View Pricing, Inventory, Delivery & Lifecycle Information: S TMicroelectronics: LIS331HH LIS331HHTR
 Datasheet下载
Datasheet下载